
It might be worth looking at Swift Codable to do this. Description given in Whats new in Swift 4? Section 3 of Udemy Course Practical iOS 11 by Stephen DeStefano See also Swift Encoders
Using the TWIT.tv podcast feed as an example: http://feeds.twit.tv/mbw.xml
Level 1 of the XML Feed (Your feed may vary)

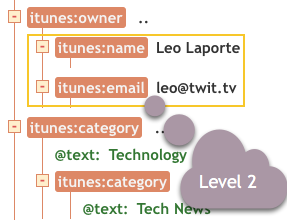
And a little deeper gives level 2.
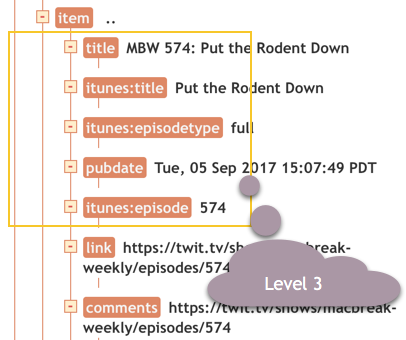
And down one more level to get to the episode (item) entries.
With this approach we won't use levels but will note when we are inside the level called "item".
Start by including XMLParserDelegate in your class. Declare variable xmlParser, currentParsedElement, episode and episodes.
xmlParser is the parser method provided by Apple
currentParsedElement is used to hold the current XML element being parsed
weAreInsideAnItem is a Boolean identifying whether or not we are within the item tags. Initially set to false.
episode is an object of Class Episode (see below)
episodes is an array of Class Episode objects used to hold the output of the parsing operation.
formatter is a DateFormatter used to transform the pubDate element from a string into a Date. The date format can be defined in the viewDidLoad function with
formatter.dateFormat = "EEE, dd MMM yyyy HH:mm:ss zzz".
class PodcastsViewController: NSViewController, XMLParserDelegate
{
...
var xmlParser: XMLParser!
var currentParsedElement = ""
var weAreInsideAnItem = false
var episode = Episode()
var episodes : [Episode] = []
let formatter = DateFormatter()
...
Data is retrieved from the podcast site/website where podcast!.rssURL contains the podcast URL as a string.
func getEpisode()
{
if podcast?.rssURL != nil
{
if let url = URL(string: (podcast!.rssURL)!)
{
URLSession.shared.dataTask(with: url)
{ (data, response, error) in
if error != nil
{
print(error ?? "Error getting url data")
}
else
{
if data != nil
{
self.xmlParser = XMLParser(data: data!)
self.xmlParser.delegate = self
self.xmlParser.parse()
DispatchQueue.main.async
{
self.tableView.reloadData()
}
}
}
}
.resume()
}
}
}
This sets the parser to work on podcast feed starting from the top, looking at various entities as it moves through the feed. Various information is enclosed in tags. Tags within tags at different levels. The approach taken here is to recognize that the information for each podcast episode is enclosed with
The parser works in three stages, didStartElement, the foundCharacters and didEndElement.
didStartElement looks for opening tags and sets up the rest of the decoding. Parameters used to hold information of interest can be initialized in this function. For this example, most importantly we also set the variable tracking when we are inside an item tag. We look for the
Once we are inside level item and are looking for particular information defined with currentParsedElement variable in foundCharacters and we start to build a temporary variable string character by character. Note we don't capture the characters for the url attribute of enclosure as the full entry is captured in didStartElement.
The last function, didEndElement detects the end of the currentParsedElement tag and initializes the currentParsedElement variable for that element. We don't need to do anything for the attributed element in didEndElement either.
Once all the specified elements are collected for this episode we get to the closing item tag. Now we gather information into the episodes array for processing outside the XML parser process. Maybe add to a tableView. Each element string is placed in a component of episode the Episode class object and added, appended to episodes, declared as an array of Episode class objects. The last step is to declare the variable weAreInsideAnItem false so we can move onto the next item, episode information in the XML stream.
The Episode class
func parser(_ parser: XMLParser, didStartElement elementName: String, namespaceURI: String?, qualifiedName qName: String?, attributes attributeDict: [String : String] = [:])
{
if elementName == "item" // finds the beginning of an item - that is the
func parser(_ parser: XMLParser, foundCharacters string: String)
{
if weAreInsideAnItem
{
switch currentParsedElement
{
case "description":
entryHtmlDescription = entryHtmlDescription + string
case "pubDate":
entryDateString = entryDateString + string
case "itunes:title":
entryTitle = entryTitle + string
// case "enclosure":
// entryAudioURL = entryAudioURL + string
default:
break
}
}
}
func parser(_ parser: XMLParser, didEndElement elementName: String, namespaceURI: String?, qualifiedName qName: String?)
{
if weAreInsideAnItem
{
switch elementName
{
case "itunes:title":
currentParsedElement = ""
case "pubDate":
currentParsedElement = ""
// case "enclosure":
// currentParsedElement = ""
case "description":
currentParsedElement = ""
default:
break
}
}
...
...
if elementName == "item"
{
episode.title = entryTitle
if formatter.date(from: entryDateString) != nil
{
episode.pubDate = formatter.date(from: entryDateString)!
}
episode.audioURL = entryAudioURL
episode.htmlDescription = entryHtmlDescription
episodes.append(episode)
weAreInsideAnItem = false
}
}
class Episode
{
var title = ""
var pubDate = Date()
var htmlDescription = ""
var audioURL = ""
}
Reference:
Index
Comments, Corrections, Suggestions: David Bourne (david@boomer.org)
My iOS and tvOS Apps and iBooks